Bowel Dysfunction
Neurogenic Bowel Care
Treatment Options
Bowel Management
and Spinal Cord Injury
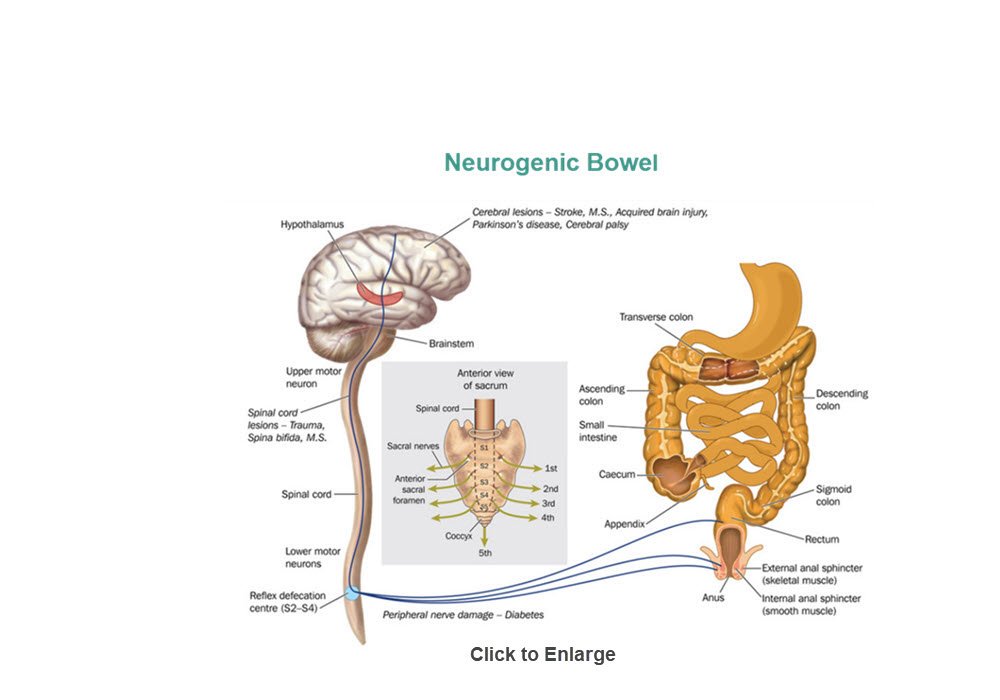
Neurogenic bowel dysfunction is characterized by alteration in normal bowel function due to the lack of nervous control. The clinical symptoms of neurogenic bowel may vary. Some clinical symptoms are bloating, constipation, and abdominal pain.
References Below
The three main implications of disruption to the motor, sensory, and autonomic pathways post spinal cord injury on bowel function are an inability to:
- Feel when the bowel is full
- Voluntarily control muscles to defecate
- Voluntarily contract muscles to prevent defecating
Neurogenic bowel dysfunction can have different neuropathological patterns in individuals with Spinal Cord Injury
Neurogenic Bowel Dysfunction
Be Active!
Key Points about Neurogenic Bowel
Function
Neurogenic bowel is the loss of normal bowel function due to a nerve problem. It causes constipation and bowel accidents.
Nerve Damage
Nerve damage may be due to an injury or a health condition such as multiple sclerosis.
Symptoms
Symptoms include trouble having a bowel movement, belly pain, leaking stool, and frequent bowel movement accidents.
Testing
Tests for diagnosis may include an MRI or CT scan of your brain or spinal cord and an ultrasound of the anus.
Treatment
Treatment includes creating a bowel management program. This includes scheduled times to remove stool from the rectum.
Neurogenic Bowel
Neurogenic bowel is when there is a loss of control of the bowel as a result of damage to the nerves. When the nerves are damaged, messages are unable to arrive at the sphincter or brain like they are supposed to. Those with neurogenic bowel may not ever feel the urge to go to the bathroom.
Also, peristalsis may not occur or be diminished which can lead to constipation or accidents. Depending on the cause, neurogenic bowel can result in the sphincter musculature being spastic or flaccid. It is important to know the difference because the type of bowel program needed will depend on the muscle tone of the sphincter.
Neurogenic Bowel Care Guide
Neurogenic Bowel FAQs
Neurogenic bowel is the loss of normal bowel function.
It’s caused by a nerve problem. A spinal cord injury or a nerve disease may damage the nerves that help control the lower part of your colon. This is the part of the body that sends solid waste out of the body. This condition gets in the way of your normal ability to store and get rid of waste.
It often causes constipation and bowel accidents.
Here are some common questions and answers about Neurogenic Bowel.
Can you heal a neurogenic bowel?
Treatment of neurogenic bowel dysfunction (NBD) is initially conservative.
People with suspected bowel rupture or perforation should be transferred to surgical care, as should any patients with rectal prolapse; these conditions are associated with high morbidity and are best managed surgically.
What helps neurogenic bowel?
- Belly (abdominal) muscle training.
- Botulinum toxin to help decrease anal sphincter spasticity.
- Colostomy surgery to make an opening for stool to empty through instead of the rectum.
- Dietary changes.
- Electrical (neural) stimulation of the belly muscles.
- Exercise and activity plans.
Do laxatives help a neurogenic bowel?
Some medications that are being used for other medical conditions or symptoms may also contribute to constipation. If these additional medications cannot be eliminated, stool softeners or oral laxatives may be used to modulate stool consistency and promote stool transit. Designing a neurogenic bowel program.
What part of brain controls bowels?
Scientists call this little brain the enteric nervous system (ENS). And it’s not so little. The ENS is two thin layers of more than 100 million nerve cells lining your gastrointestinal tract from the esophagus to rectum.
What causes neurogenic bowel dysfunction?
A spinal cord injury sometimes interrupts communication between the brain and the nerves in the spinal cord that control bladder and bowel function. This can cause bladder and bowel dysfunction known as neurogenic bladder or neurogenic bowel. People with multiple sclerosis or spina bifida might have similar problems.
Which spinal nerve controls bowels?
Sacral nerves are located in the pelvic area just above the tailbone. These nerves control the muscles and organs that contribute to overall bowel control, such as the anal sphincter and pelvic floor.
Getting A Diagnosis
With better access to information, unfortunately, many people will try to diagnose themselves without seeing a doctor.
Even if you are confident from your own research above that you have neurogenic bowel, it is imperative that you see your primary care physician or gastroenterologist.
Only a doctor can provide you with a diagnosis after reviewing your medical history, completing a physical exam and/or reviewing the results of tests that can be performed.
Neurogenic bowel is the loss of normal bowel function. It’s caused by a nerve problem and needs to be analyzed by a doctor.
Popular Blog Posts
Colonoscopy
A very well-done video by Cedars Sinai.
Effective Bowel Care Management
A bowel care management program must work best for you!
Spinal Cord Injuries
Learn about the most common types of spinal cord injuries and how they impact the function of the body.
References
[1] Stiens SA, Bergman SB, Goetz LL. Neurogenic bowel dysfunction after spinal cord injury: clinical evaluation and rehabilitative management. Archives of physical medicine and rehabilitation. 1997 Mar 1;78(3):S86-102.
[2] Deng Y, Dong Y, Liu Y, Zhang Q, Guan X, Chen X, Li M, Xu L, Yang C. A systematic review of clinical studies on electrical stimulation therapy for patients with neurogenic bowel dysfunction after spinal cord injury. Medicine. 2018 Oct;97(41).